Linux is based on the UNIX operating system. UNIX is a powerful, multi-user, multitasking operating system originally developed in the 1970s at AT&T Bell Labs. It laid the foundation for many modern operating systems, including Linux.
- Linux is free and open-source, accessible to everyone.
- This promotes global collaboration and innovation.
- Linux offers efficient performance and strong security.
- It works well across many devices and industries.
Linux combines a wide range of open-source tools and components to form a complete computing environment. These components include file systems, user interfaces, system utilities, and application programs all working together to manage hardware and enable users to interact with their computer systems.
Architecture of Linux
Linux architecture refers to the layered structure of the Linux operating system that defines how its components - such as the kernel, shell, system libraries, and hardware - interact with each other to manage system resources and execute user programs efficiently. It has the following components:
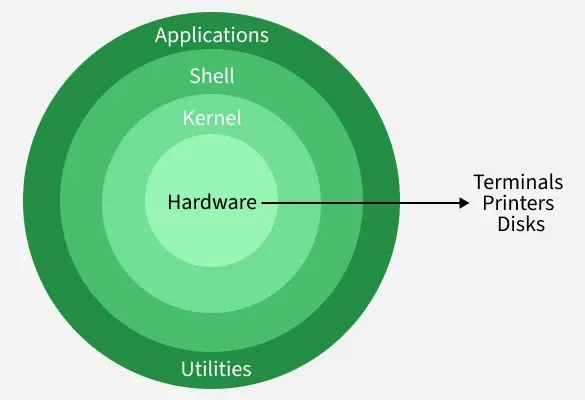
1. Kernel
The kernel is the core of the Linux operating system that manages hardware resources and controls communication between software and hardware.
- Handles process management, memory, and device control.
- Prevents conflicts between multiple running programs.
Types of Kernels: Monolithic, Microkernel, Hybrid, Exokernel
2. System Libraries
System libraries provide essential functions that allow applications to interact with the kernel without needing to access it directly.
- Contain reusable pre-written code for common system operations.
- Act as an interface between applications and the Linux kernel.
3. Shell
The shell is the command-line interface that allows users to communicate with the operating system by entering commands.
- Interprets and executes user commands.
- Acts as a bridge between user actions and kernel processing.
4. Hardware Layer
The hardware layer consists of physical components that execute commands and provide system resources.
- Includes CPU, RAM, storage, and input/output devices.
- Communicates with the OS using device drivers and kernel services.





0 comments:
Post a Comment